As technology continues to advance, the way humans interact with computers is evolving beyond keyboards, mice, and touchscreens. Brain-Computer Interaction (BCI) represents the next frontier in human-computer interfaces (HCI), enabling direct communication between the human brain and external devices. BCIs promise to revolutionize computing, healthcare, gaming, and even communication, making interactions faster, more intuitive, and more immersive.
Understanding Brain-Computer Interaction
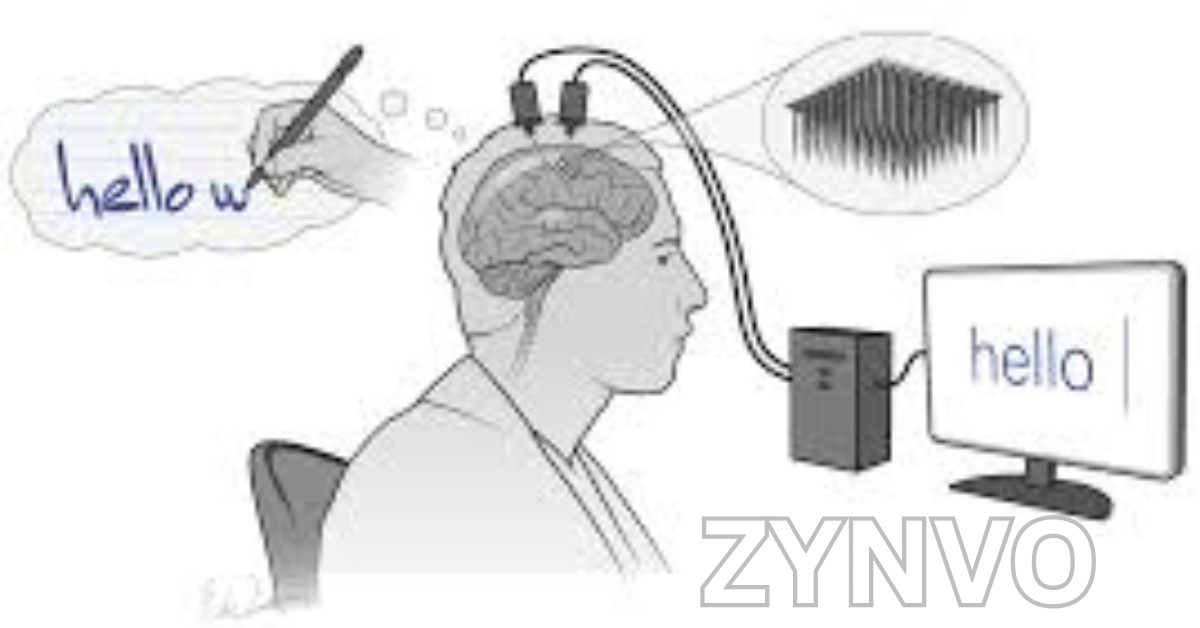
Brain-Computer Interaction, or BCI, is a technology that allows direct communication between the brain and a computer system, bypassing traditional input methods. BCIs measure brain activity, interpret neural signals, and translate them into commands that control external devices.
Types of BCIs
-
Invasive BCIs
-
Electrodes are implanted directly into the brain.
-
Offer high signal accuracy but involve surgical risks.
-
-
Partially Invasive BCIs
-
Electrodes are placed inside the skull but not in brain tissue.
-
Balance between signal quality and lower medical risk.
-
-
Non-Invasive BCIs
-
Use external devices like EEG (electroencephalography) caps to measure brain signals.
-
Safe and easy to use but less precise than invasive methods.
-
How BCIs Work
The process of BCI typically involves the following steps:
-
Signal Acquisition
-
Brain activity is recorded using electrodes or sensors.
-
Signals include electrical impulses from neurons, such as alpha, beta, and gamma waves.
-
-
Signal Processing
-
Raw neural signals are filtered to remove noise and artifacts.
-
Machine learning algorithms interpret these signals to identify user intent.
-
-
Translation into Commands
-
Processed signals are converted into actionable commands.
-
Commands can control a computer cursor, robotic arm, wheelchair, or other devices.
-
-
Feedback
-
The system provides feedback to the user, which can be visual, auditory, or tactile.
-
Feedback helps improve control and accuracy over time.
-
Applications of Brain-Computer Interaction
1. Medical and Assistive Technology
-
BCIs offer life-changing solutions for individuals with disabilities.
-
Paralyzed patients can control wheelchairs, robotic limbs, or speech devices using brain signals.
-
Neurological rehabilitation uses BCIs to retrain motor functions in stroke patients.
2. Gaming and Entertainment
-
BCIs can create immersive gaming experiences where players control actions using thoughts.
-
Enhances virtual reality (VR) experiences, making them more intuitive.
3. Communication Enhancement
-
Enables communication for patients with severe speech impairments.
-
“Thought-to-text” systems convert neural signals into written or spoken words.
4. Workplace Productivity
-
BCIs can monitor cognitive load, focus, and stress levels.
-
Adaptive interfaces can optimize workflows based on brain activity.
5. Military and Aerospace Applications
-
BCIs can control drones or robotic systems in high-risk environments.
-
Enhances situational awareness and reduces reaction time in critical missions.
Graph: Projected Growth of BCI Market (2020–2030)
(Demonstrates rapid market growth due to increasing adoption in healthcare, gaming, and defense.)
Benefits of BCIs
-
Enhanced Accessibility
-
Provides control options for people with severe physical limitations.
-
Faster Interaction
-
Eliminates intermediaries like keyboards or touchscreens, enabling direct thought-based control.
-
Improved Cognitive Understanding
-
BCIs help researchers understand brain functions, cognition, and neurological disorders.
-
Integration with AI
-
AI algorithms enhance signal processing and interpretation, making BCIs more accurate and adaptive.
-
Immersive Experiences
-
BCIs revolutionize entertainment, VR, and AR by providing thought-controlled interactions.
Challenges in Brain-Computer Interaction
-
Signal Accuracy and Noise
-
Non-invasive BCIs face challenges in accurately capturing brain signals due to interference and low resolution.
-
Ethical Concerns
-
Privacy of neural data is critical; misuse could lead to unauthorized access to thoughts.
-
Consent and data ownership issues are still evolving.
-
Medical Risks (for Invasive BCIs)
-
Implantation surgery carries risks such as infection or tissue damage.
-
Cost and Accessibility
-
Advanced BCIs remain expensive, limiting widespread adoption.
-
User Training
-
Users need training to effectively control devices through brain signals.
Future Trends in Brain-Computer Interaction
1. Non-Invasive BCI Advancements
-
EEG and fNIRS technologies are improving in accuracy and portability.
-
Goal: high-performance BCIs without surgical intervention.
2. AI-Driven Signal Interpretation
-
Machine learning models will make BCIs faster and more reliable.
-
Can predict user intent even with weak or noisy signals.
3. Integration with Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
-
BCIs will allow thought-driven navigation in VR environments.
-
Potential for immersive education, training, and gaming experiences.
4. Brain-to-Brain Communication
-
Experimental BCIs are exploring direct communication between two brains.
-
Could revolutionize collaborative work and remote communication.
5. Consumer Adoption
-
Wearable BCI devices for gaming, meditation, productivity, and wellness.
-
Increased affordability and miniaturization will drive mass-market adoption.
Case Studies of BCI Implementation
1. Neuralink
-
Elon Musk’s company is developing high-bandwidth invasive BCIs.
-
Goal: allow paralyzed patients to regain movement and enable human-AI symbiosis.
2. Emotiv Systems
-
Produces non-invasive EEG headsets for research, education, and consumer applications.
-
Supports mental state monitoring, gaming, and neurofeedback.
3. BrainGate
-
BCI system assisting paralyzed patients to control robotic arms and computers.
-
Demonstrates practical medical applications of BCIs in restoring independence.
Conclusion
Brain-Computer Interaction represents a paradigm shift in human-computer interfaces, breaking the limitations of traditional input devices. From enhancing accessibility for individuals with disabilities to creating immersive gaming and VR experiences, BCIs have far-reaching potential across industries.
While challenges such as ethical considerations, signal accuracy, and high costs remain, technological advancements in AI, non-invasive sensors, and wearable devices are making BCIs increasingly practical. The future of human-computer interaction is poised to be direct, intuitive, and thought-driven, redefining how we work, communicate, and interact with technology.
As research progresses and adoption expands, BCIs could become a common part of daily life, bridging the gap between human cognition and digital systems, and ushering in a new era of next-generation interfaces.



